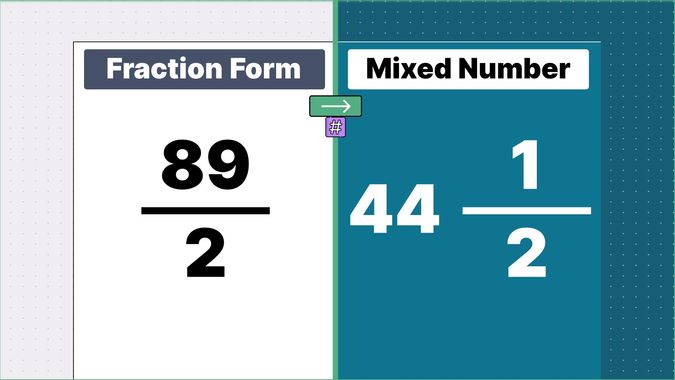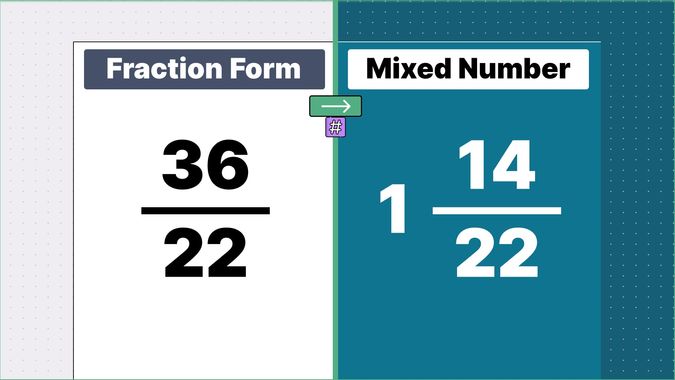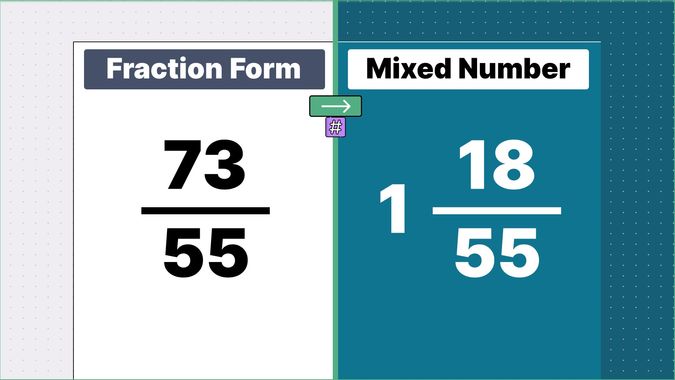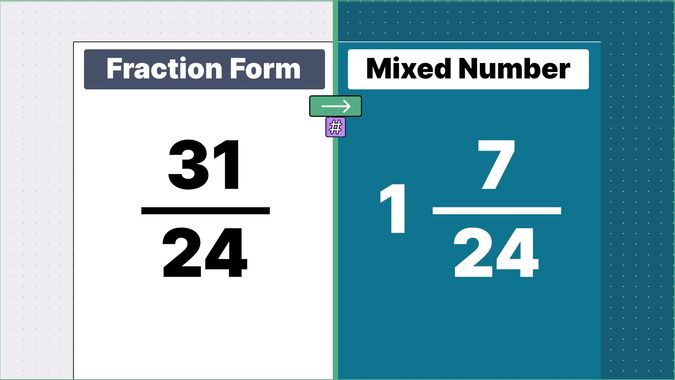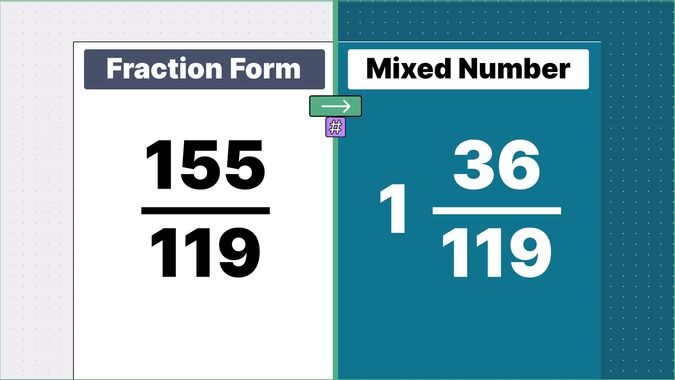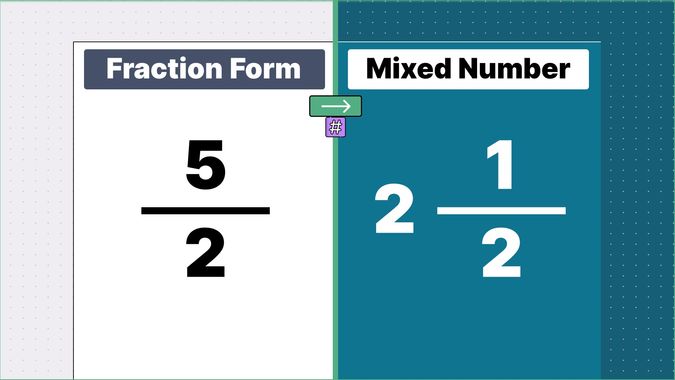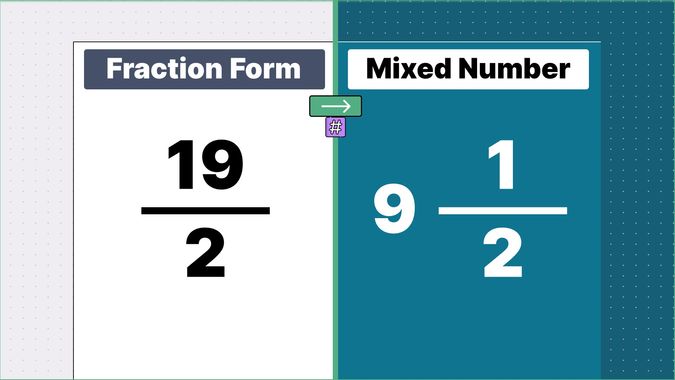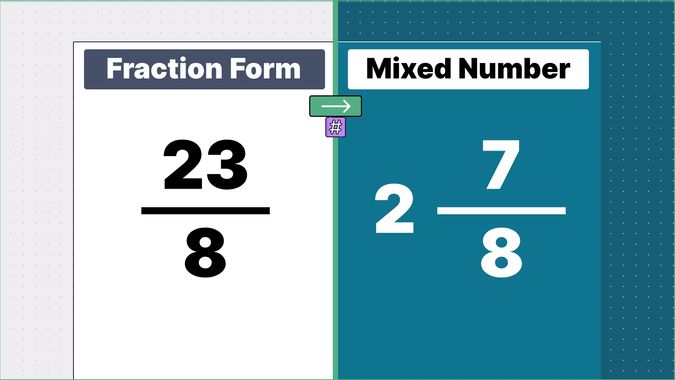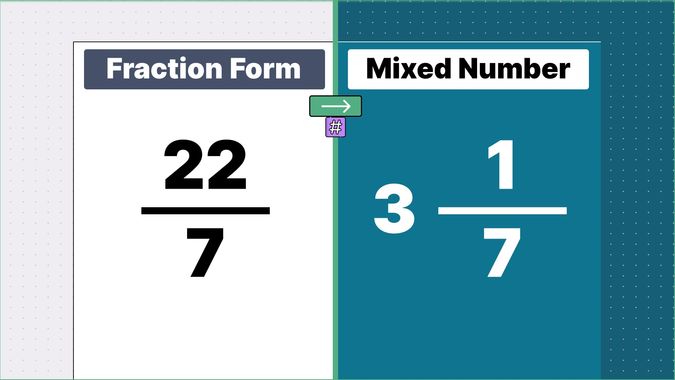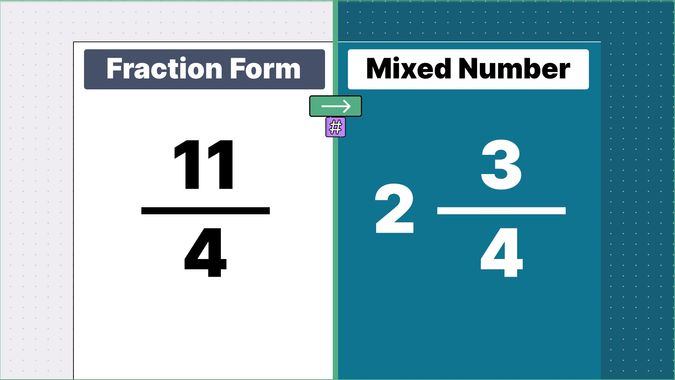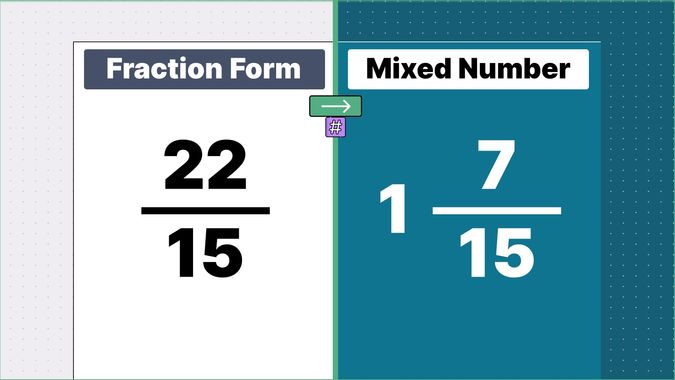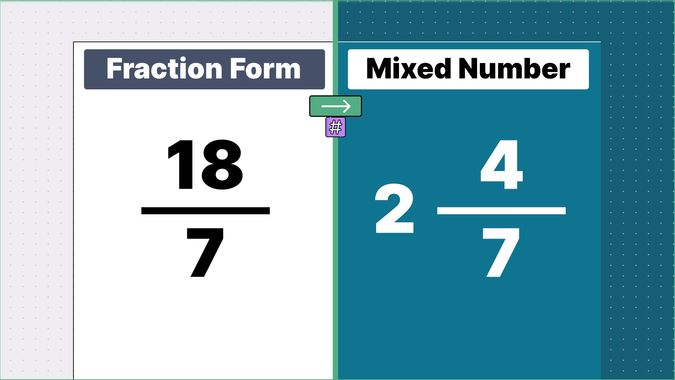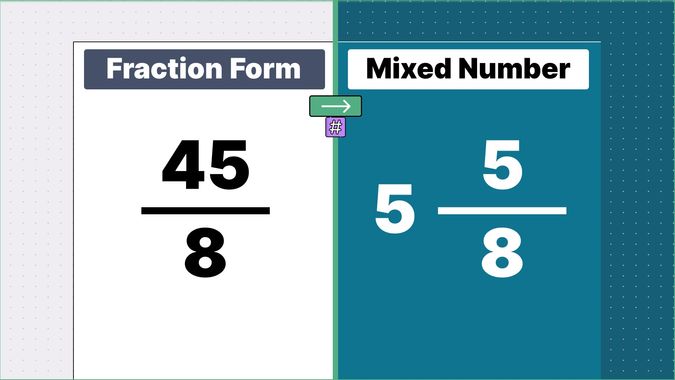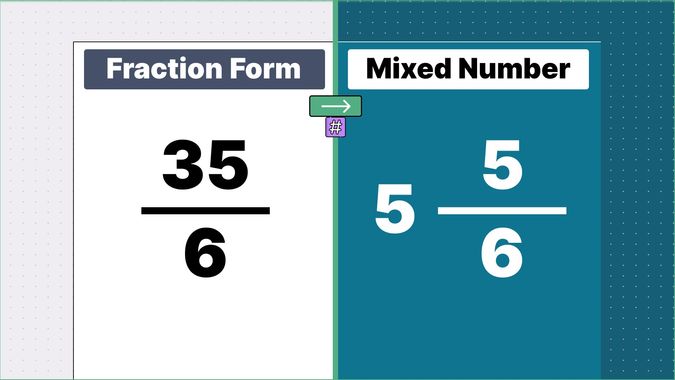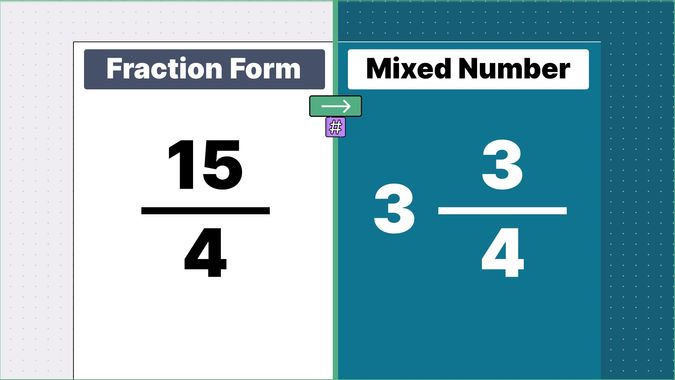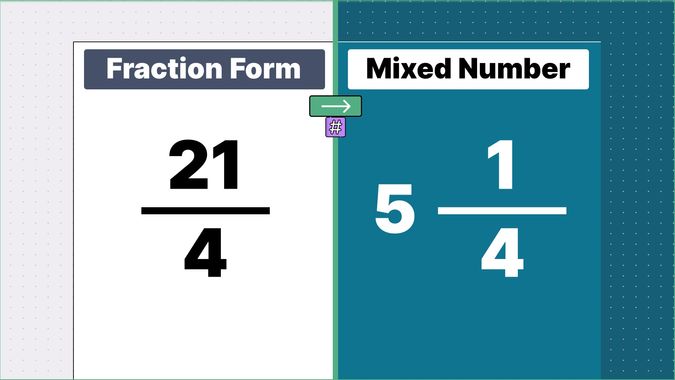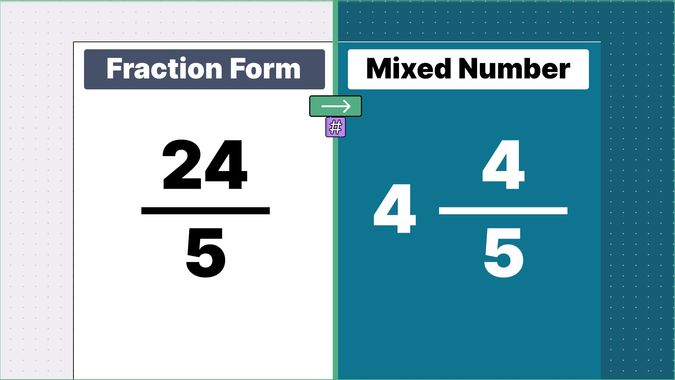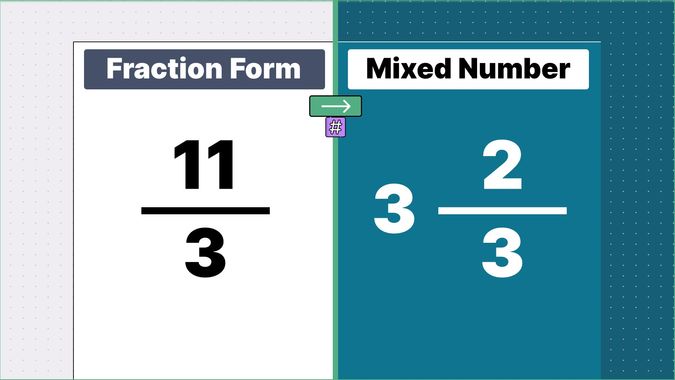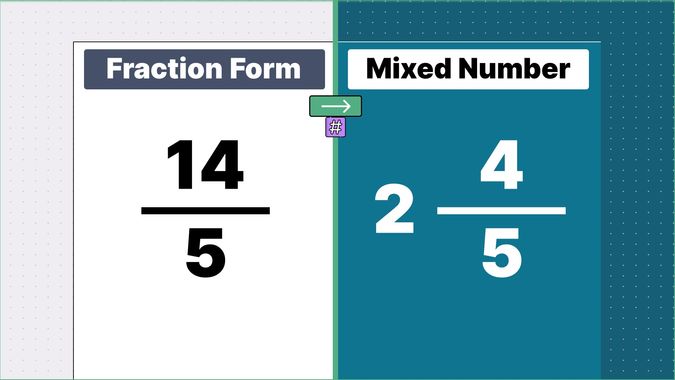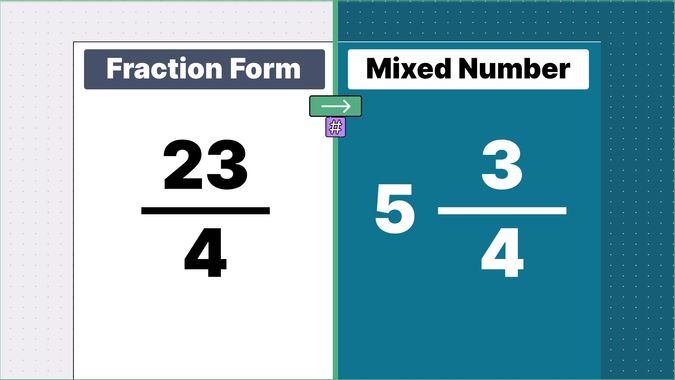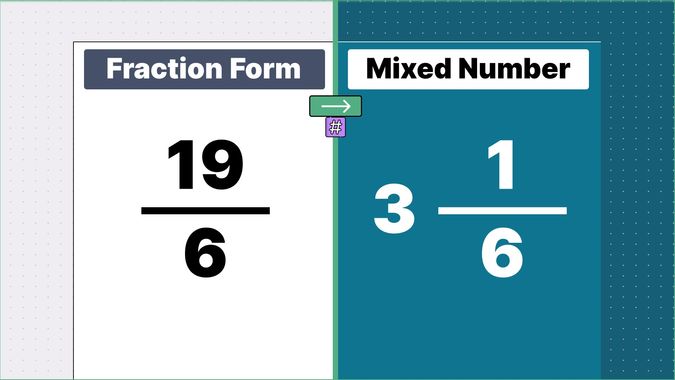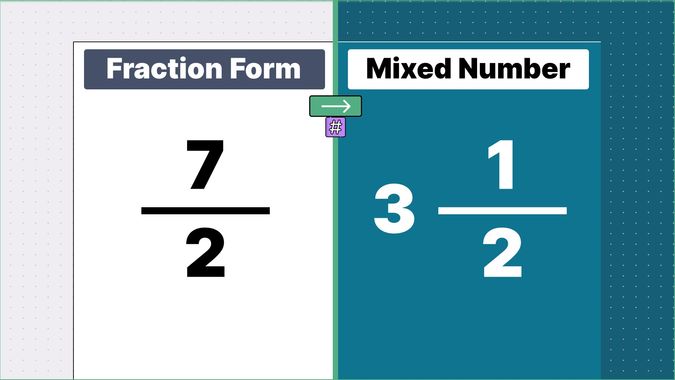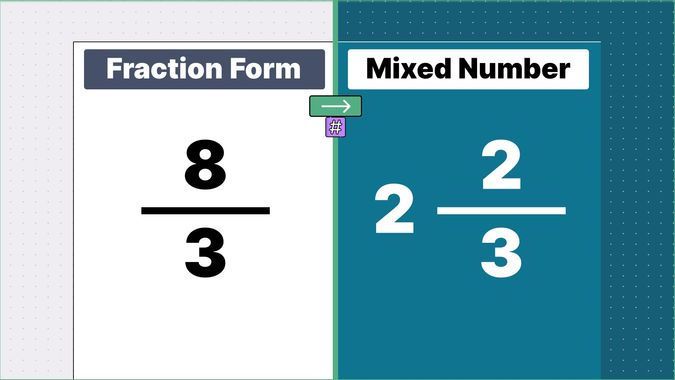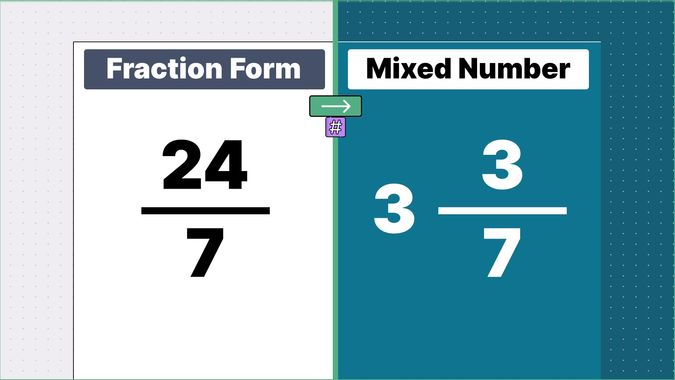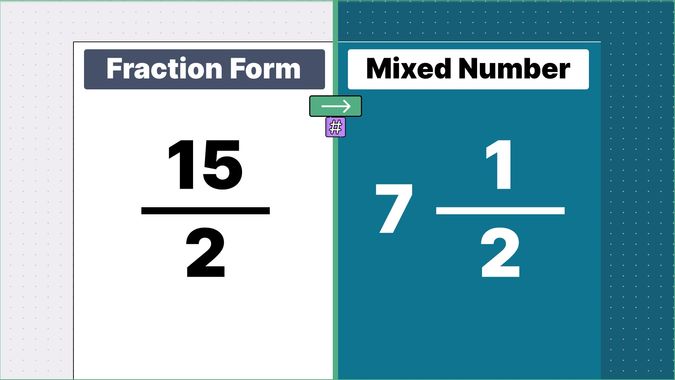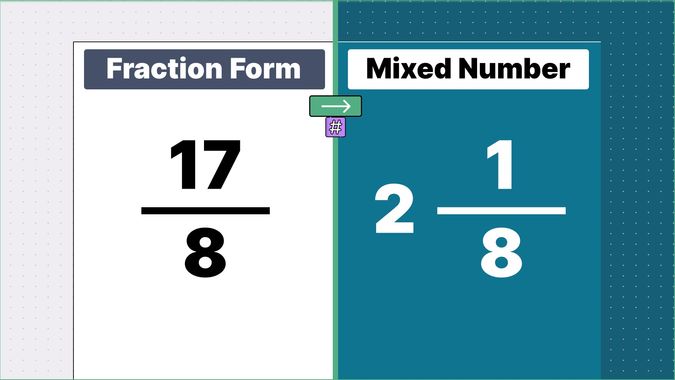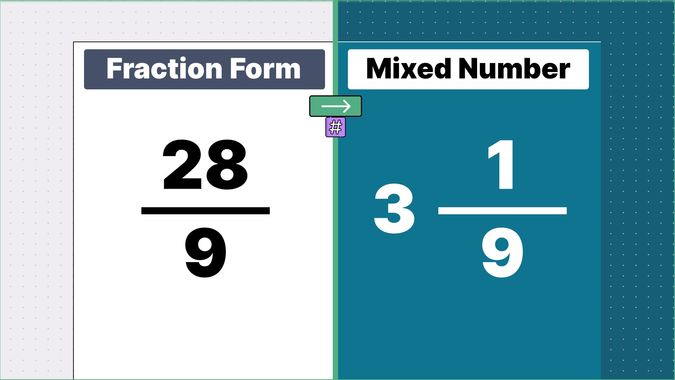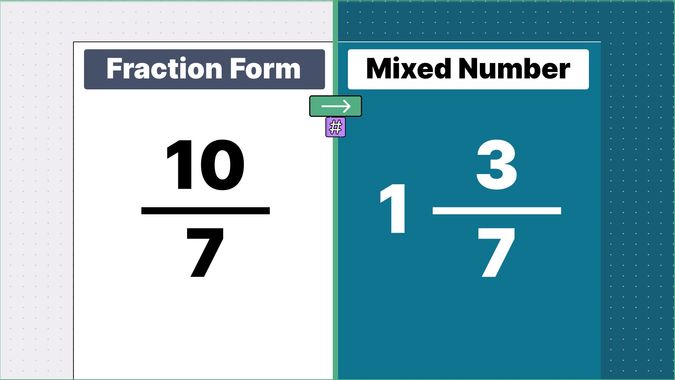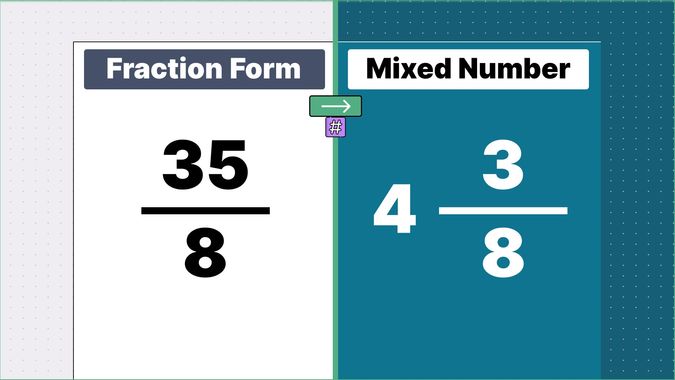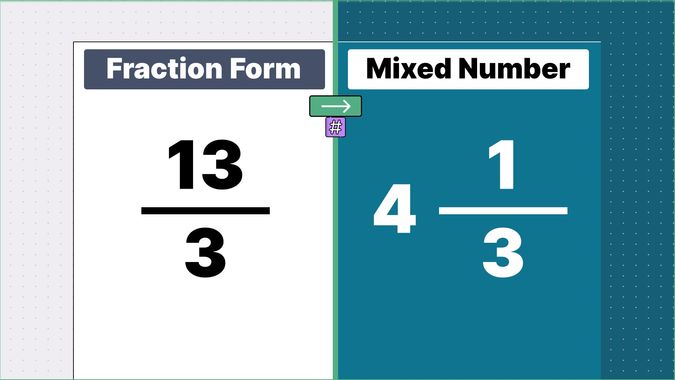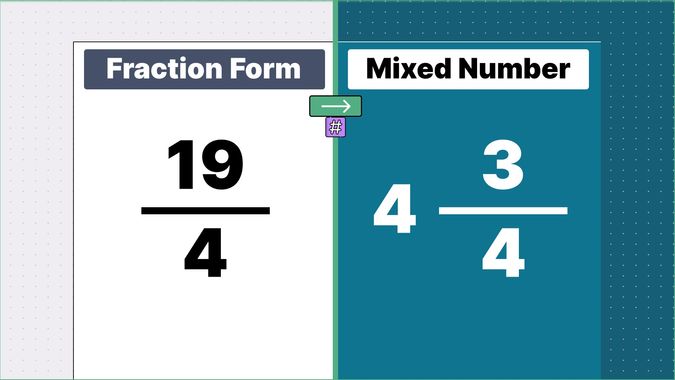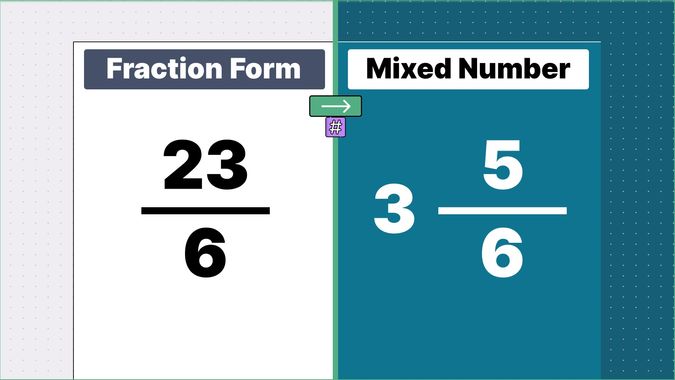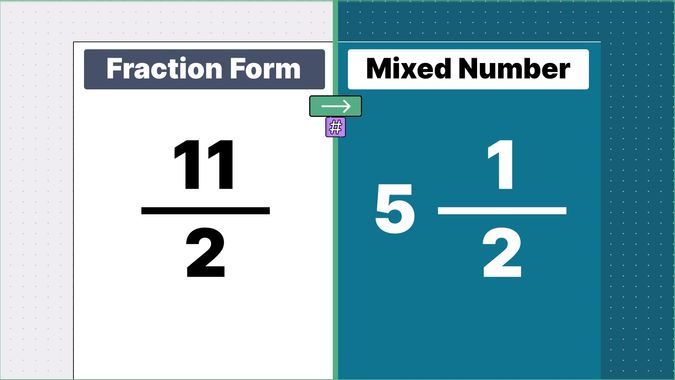
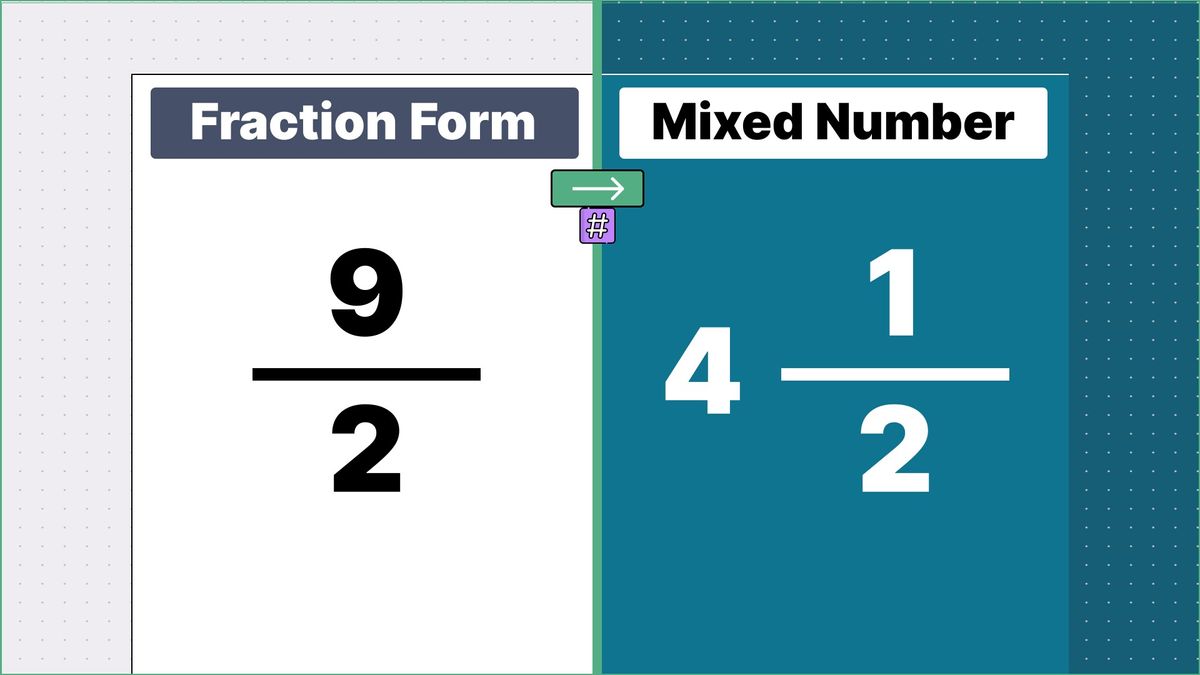
What is 9/2 as a Mixed Number?
9/2 as a mixed number is: 4 1/2
Want to calculate for other fractions? Use our online Fraction to Mixed Number calculator .
How did we get this answer?
When we come across a fraction like 9/2, it's often easier to understand or visualize it when it's expressed as a mixed number. A mixed number is a number made up of a whole number and a proper fraction.
What is a Mixed Number?
To begin with, let's first clarify what a mixed number is:
- Whole Number: A number without any fractions.
- Proper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator.
Mixed Number: A combination of a whole number and a proper fraction.
Converting 9/2 into a Mixed Number
-
Division: Divide
9by2.-
This means when you divide
9by2, you get a quotient of4with a remainder of1.
-
This means when you divide
-
Formulate the Mixed Number:
- The quotient becomes the whole number.
- The remainder becomes the new numerator of the proper fraction, while the original denominator remains unchanged.
Examples for Clarity:
To understand the process more thoroughly, let’s take a look at a few examples with different fractions and their mixed number conversions.
-
Example 1: Convert 6/3 into a mixed number.
-
Division: When we divide 6/3:
- The quotient is 2.
- The remainder is 0.
-
Mixed Number Representation: The quotient becomes the whole number, and the
remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction part. The denominator remains the same.
- Result: 2 0/3.
-
Division: When we divide 6/3:
-
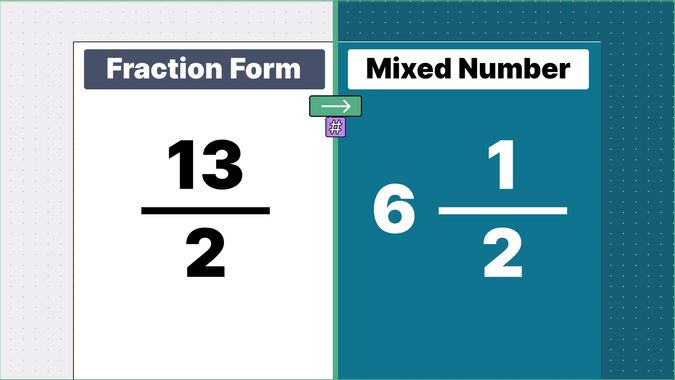
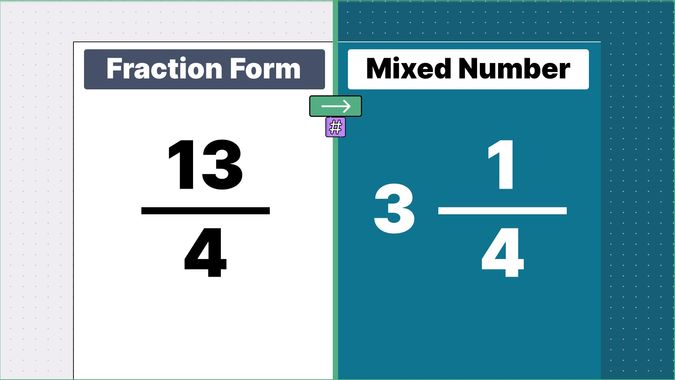
Example 2: Convert 13/4 into a mixed number.
-
Division: When we divide 13/4:
- The quotient is 3.
- The remainder is 1.
-
Mixed Number Representation: The quotient becomes the whole number, and the
remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction part. The denominator remains the same.
- Result: 3 1/4.
-
Division: When we divide 13/4:
-
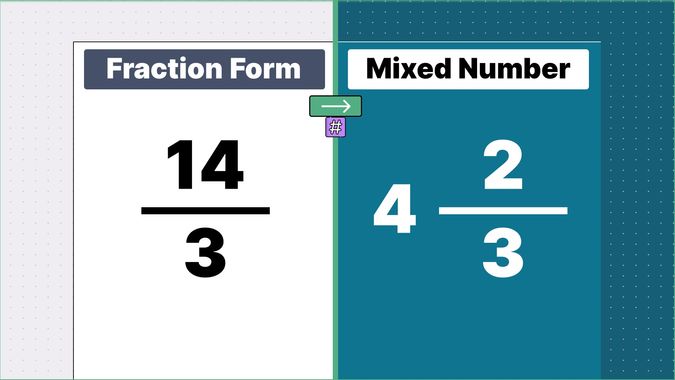
Example 3: Convert 14/3 into a mixed number.
-
Division: When we divide 14/3:
- The quotient is 4.
- The remainder is 2.
-
Mixed Number Representation: The quotient becomes the whole number, and the
remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction part. The denominator remains the same.
- Result: 4 2/3.
-
Division: When we divide 14/3:
Why Use Mixed Numbers?
- Easier Visualization: It's simpler to visualize certain items in the format of mixed numbers than improper fractions.
- Practical Applications: When measuring or dividing items in real-world scenarios, it often makes more sense to use whole numbers combined with fractions, rather than unwieldy improper fractions.
In conclusion, converting improper fractions into mixed numbers can offer a more intuitive understanding, especially in practical contexts. It’s just another way mathematics offers us to understand and interpret the world around us.
Want to represent another fraction as a mixed number without the manual hassle? Use our dedicated Fraction to Mixed Number Calculator .
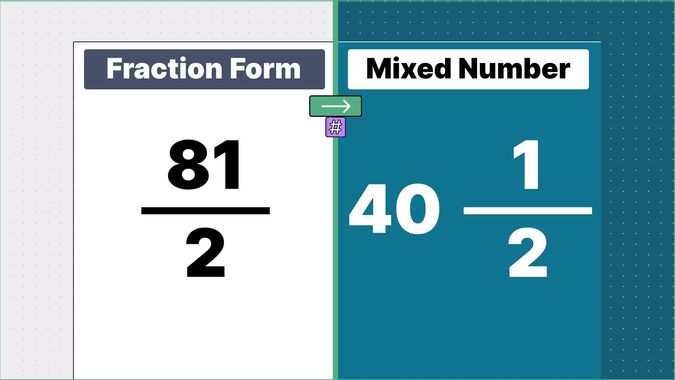
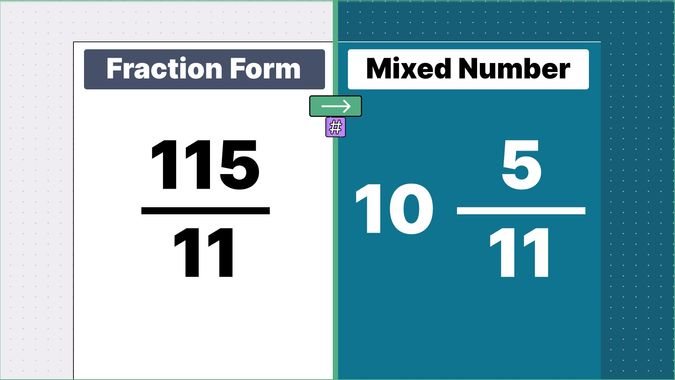
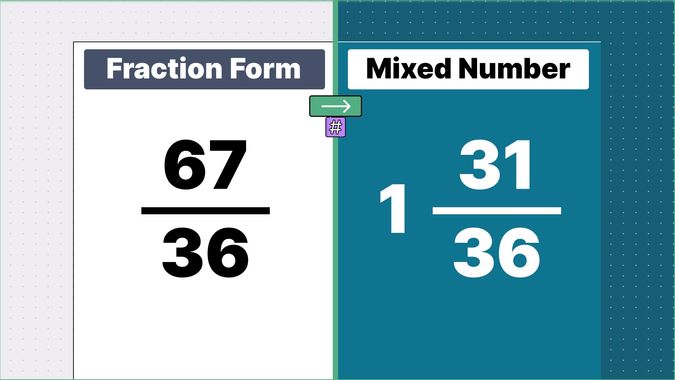
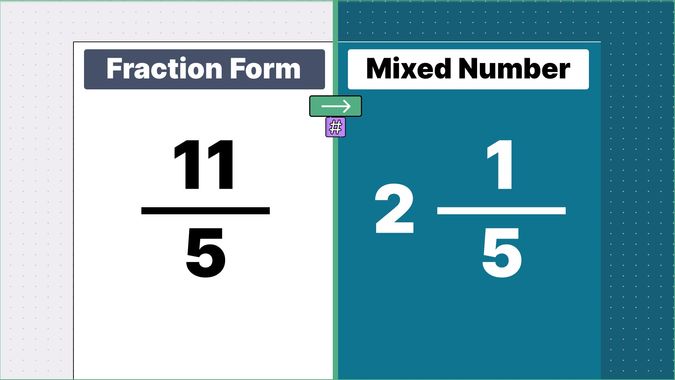
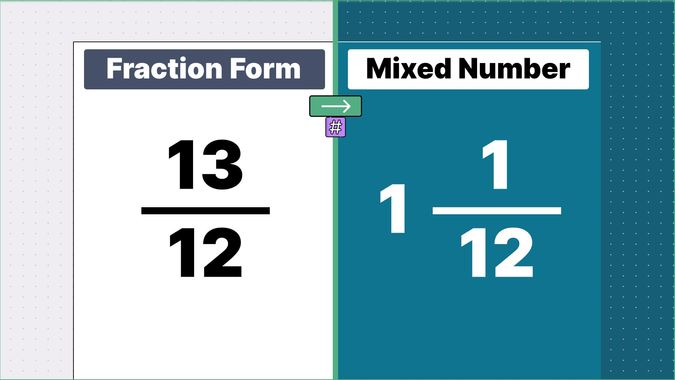
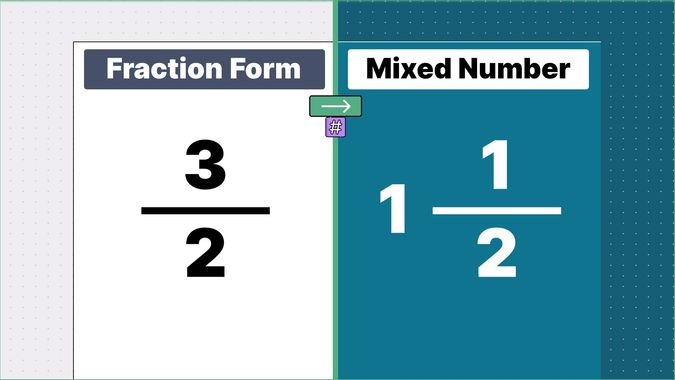
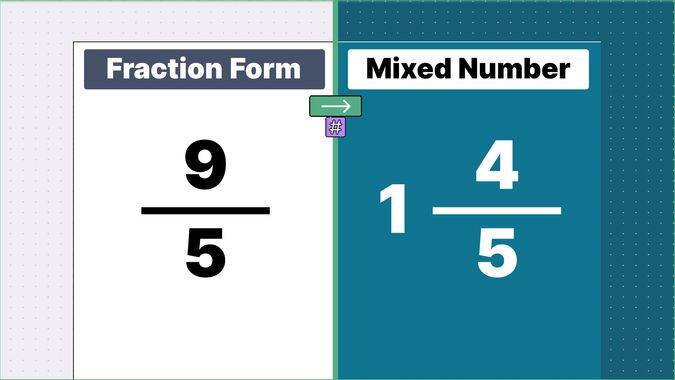
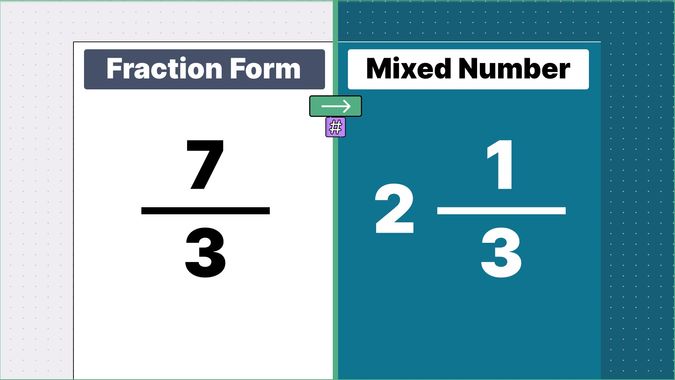
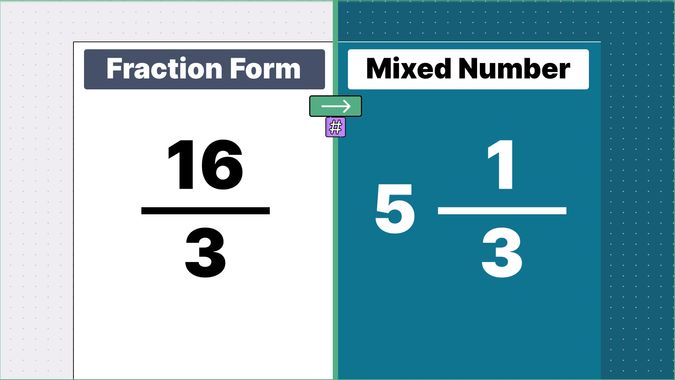
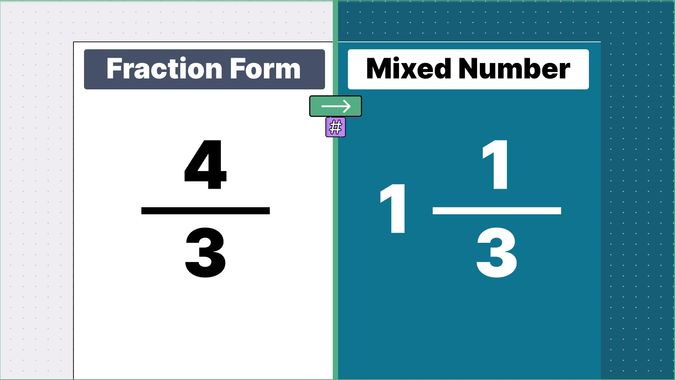
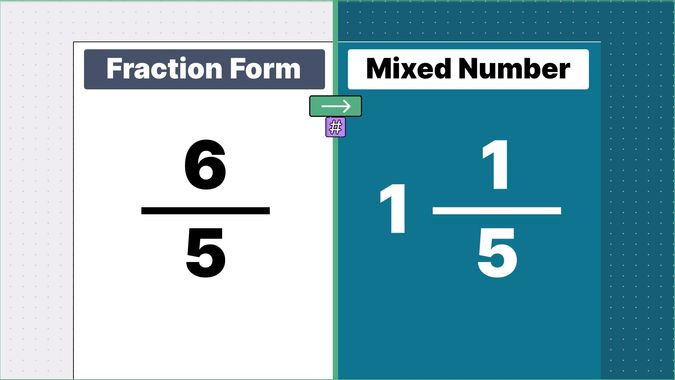
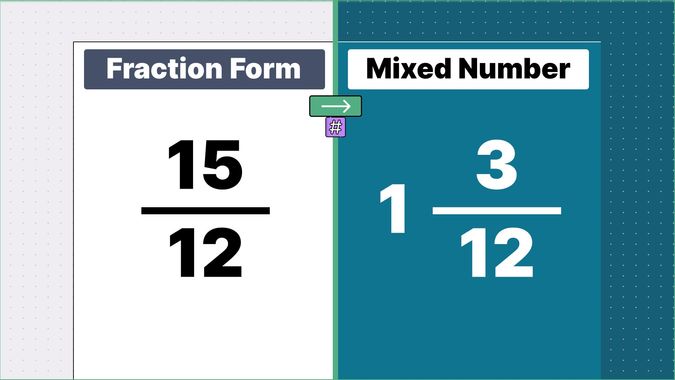
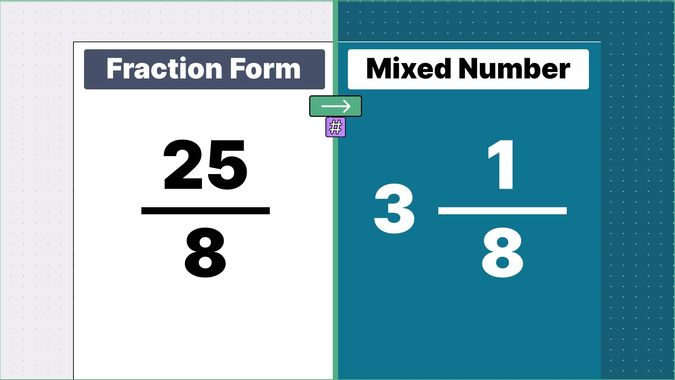
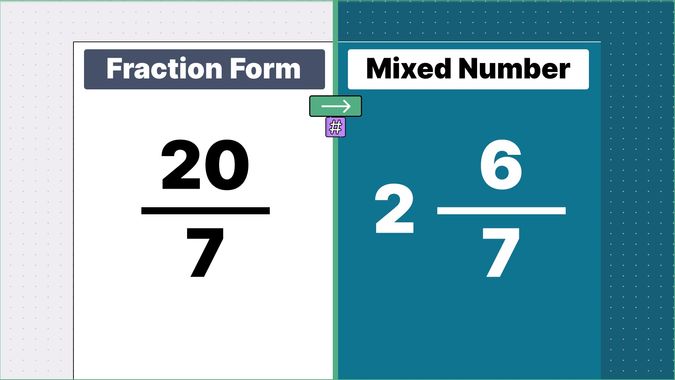
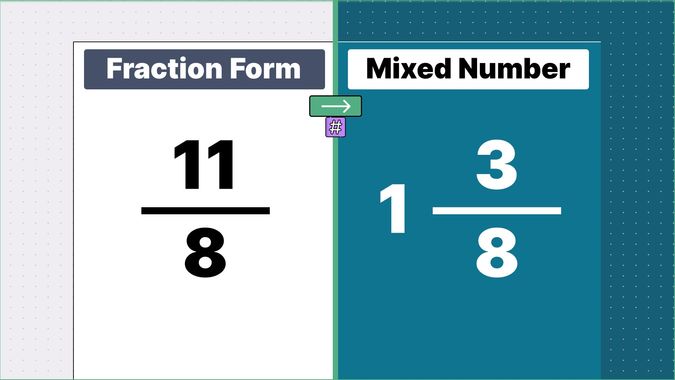
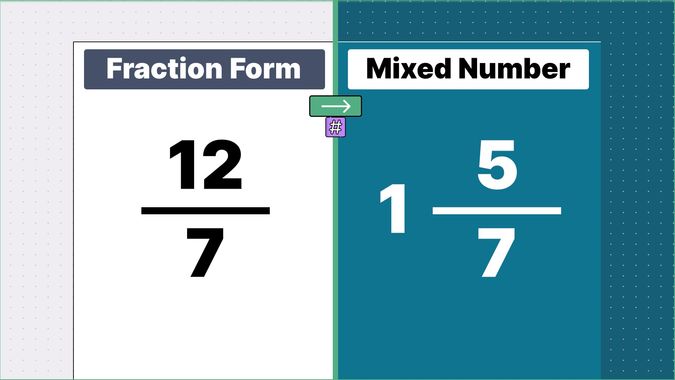
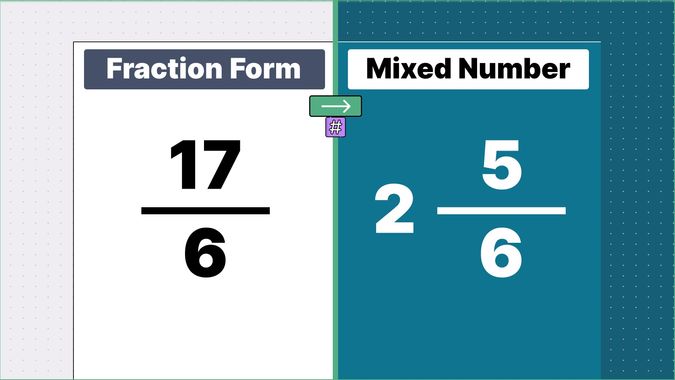
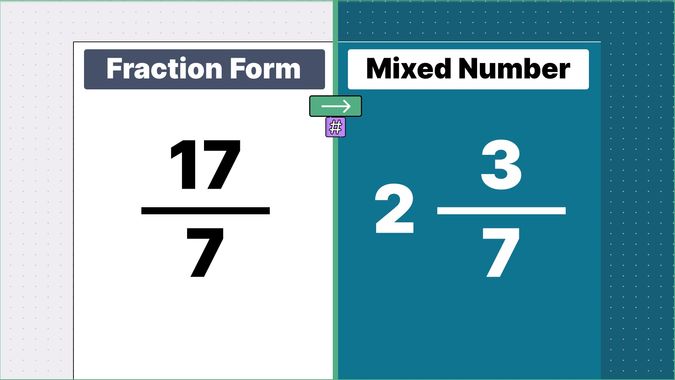
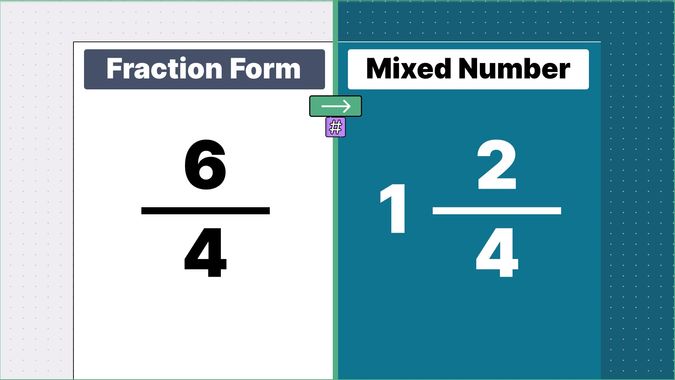
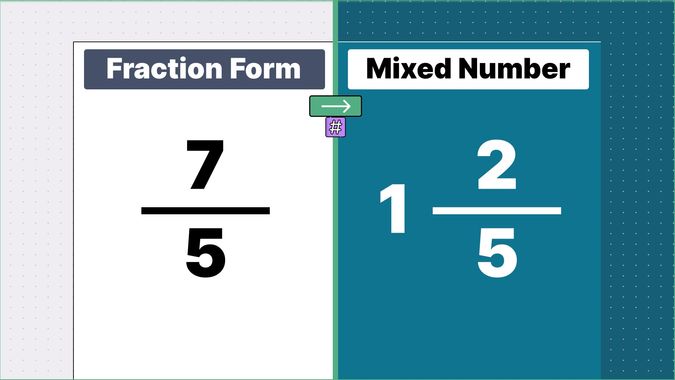
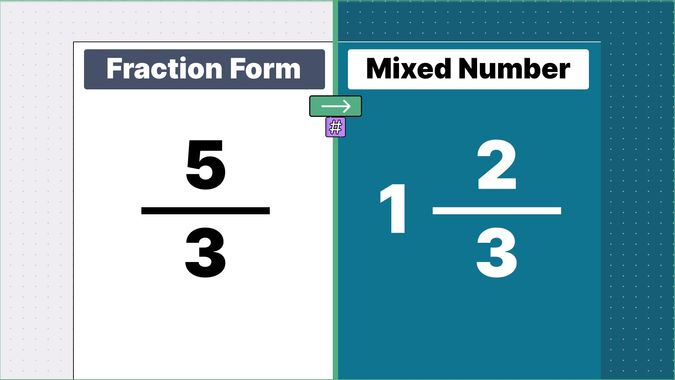
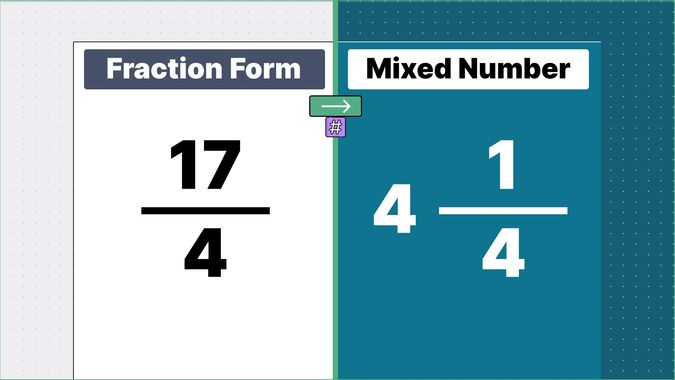
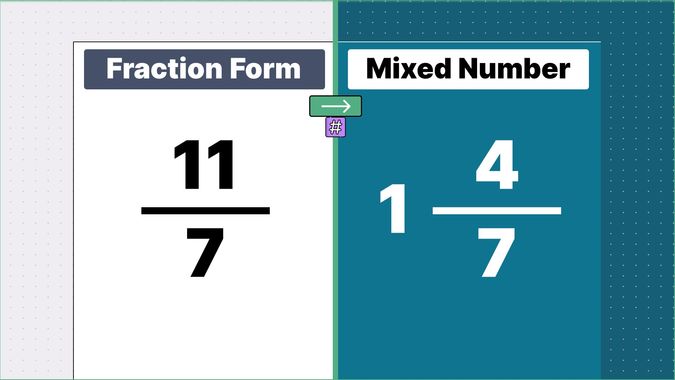
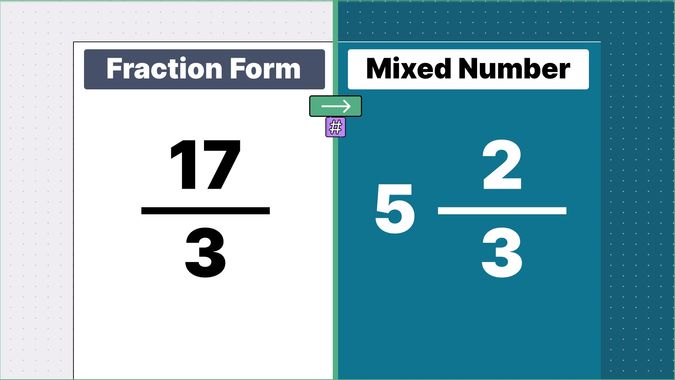
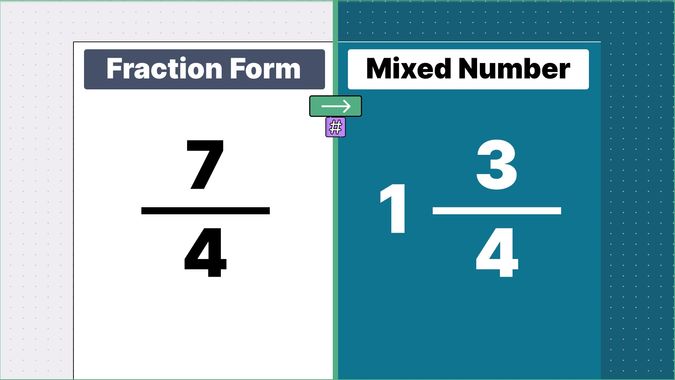
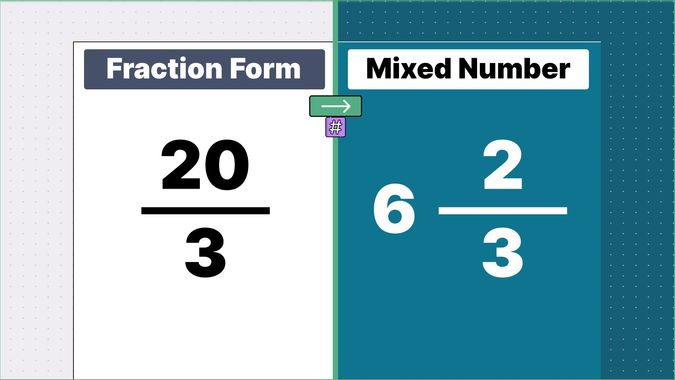
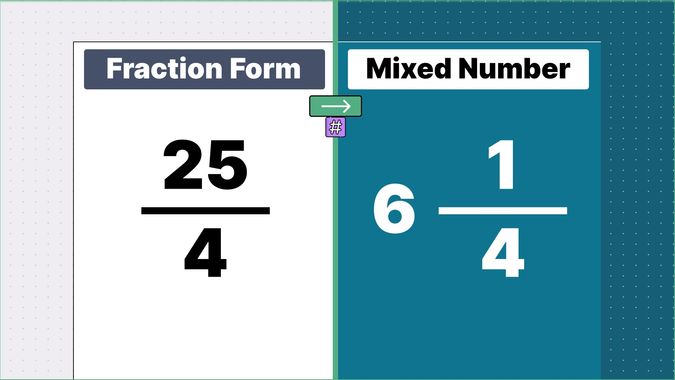
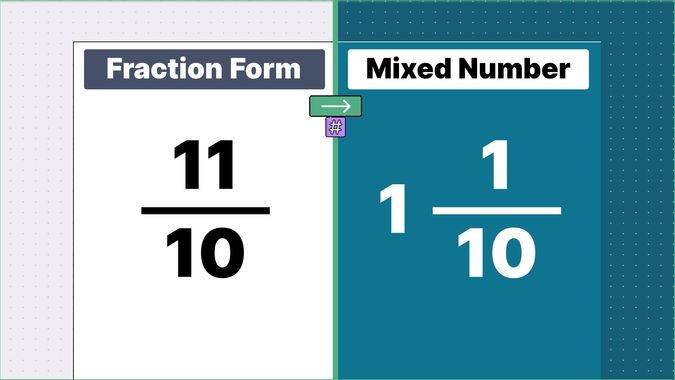
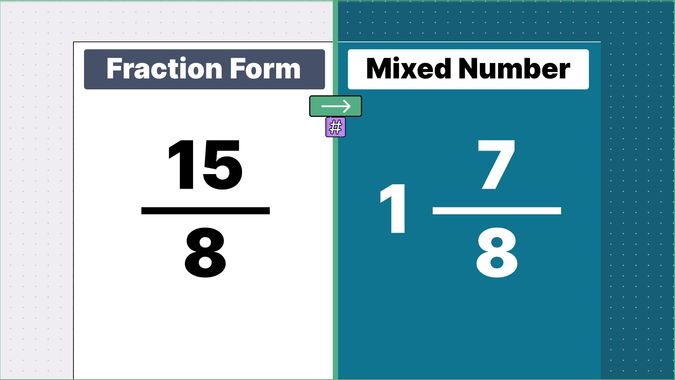
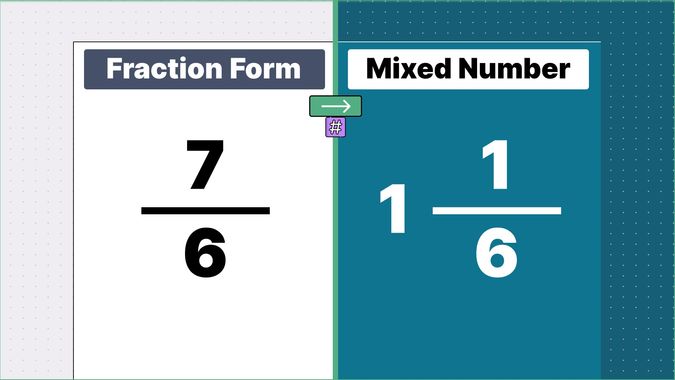
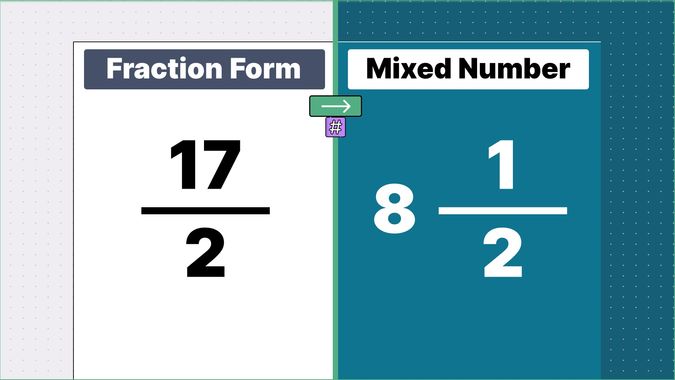
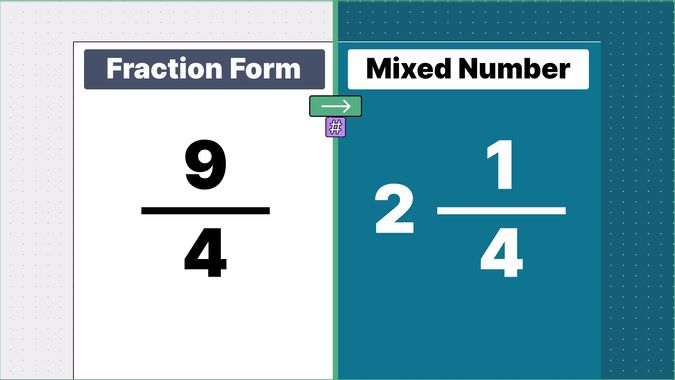
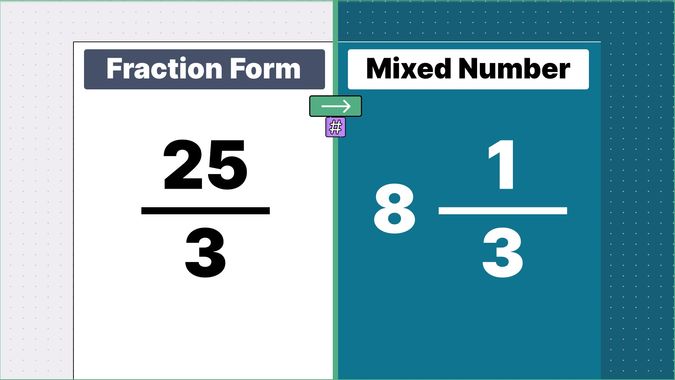
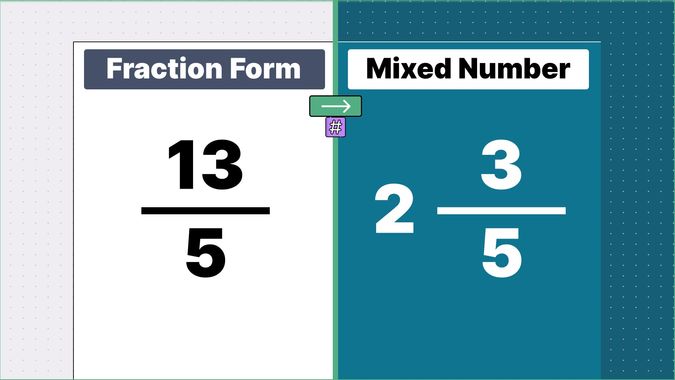
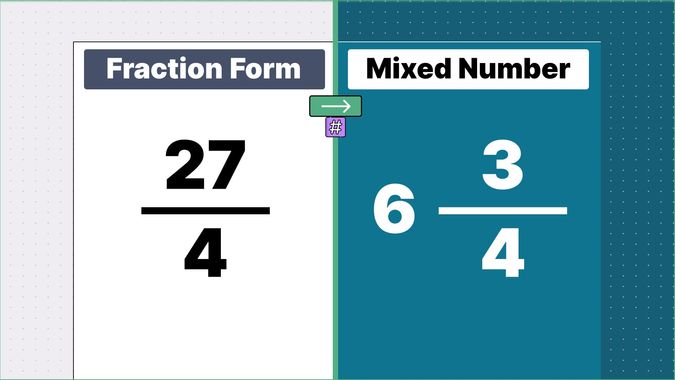
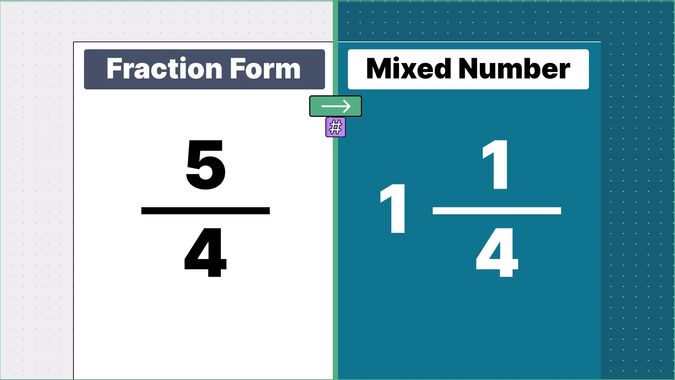
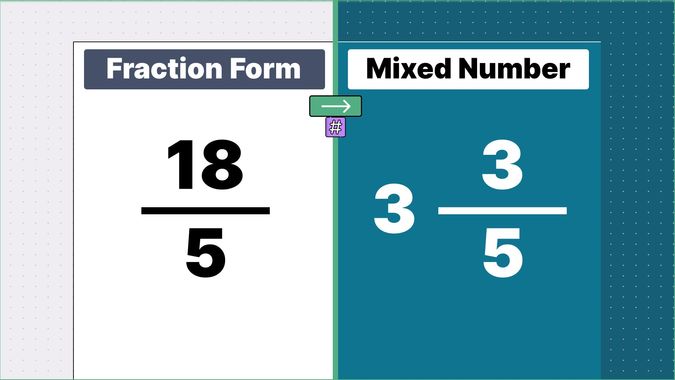
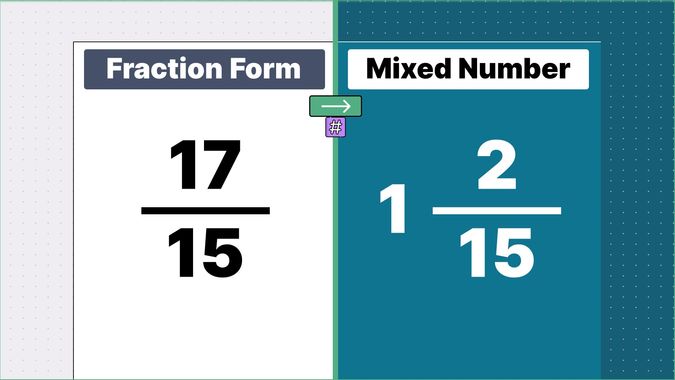
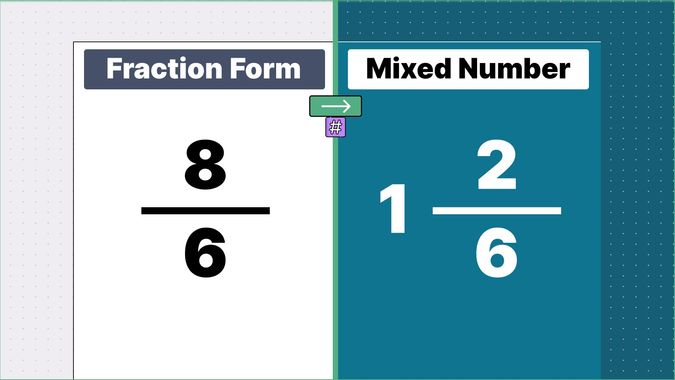
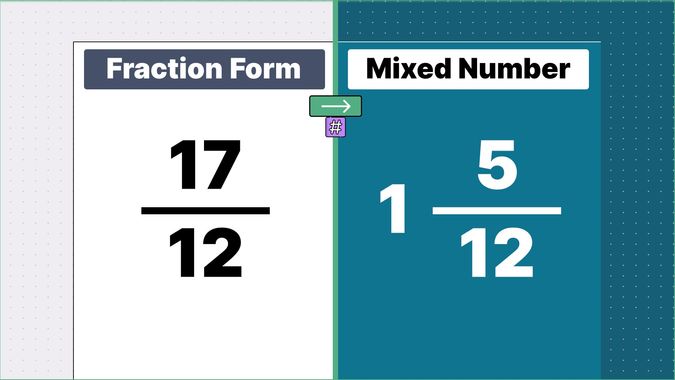
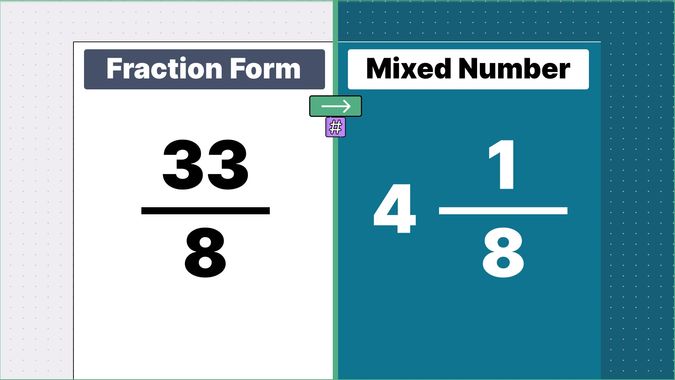
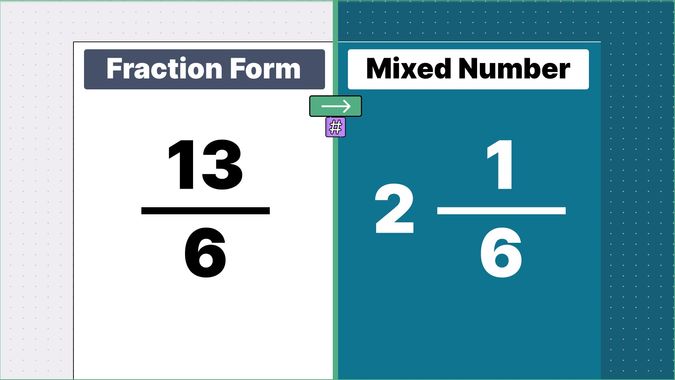
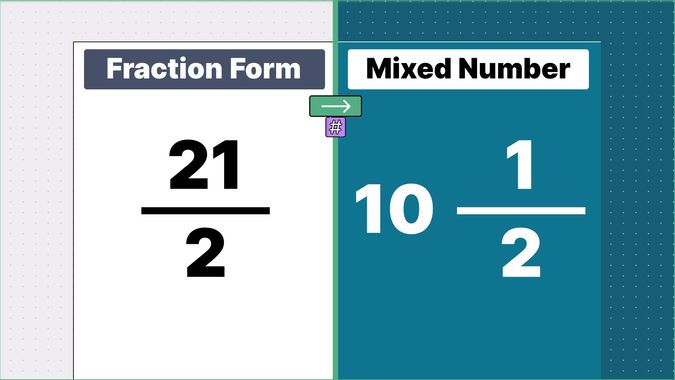
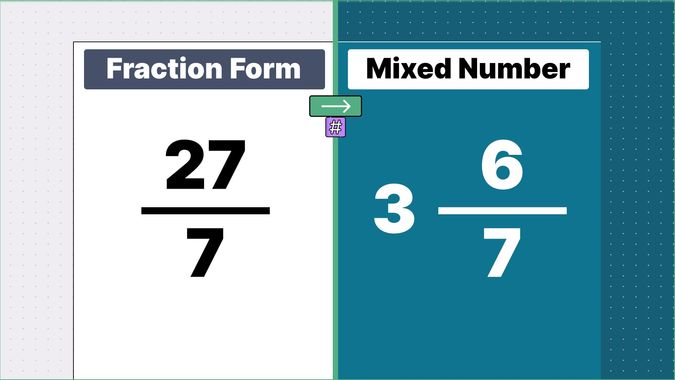
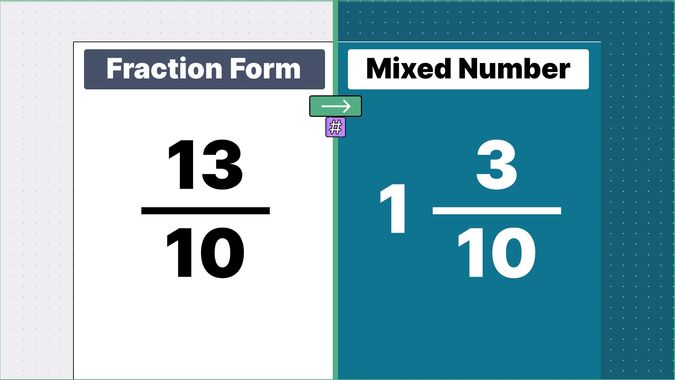
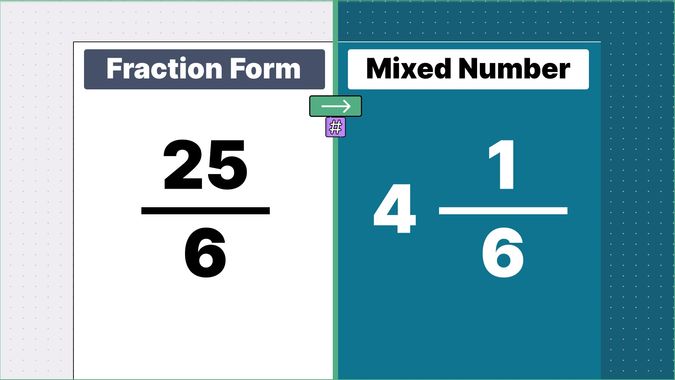
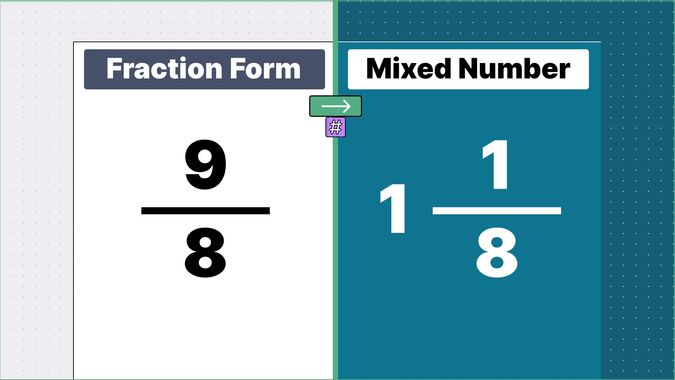
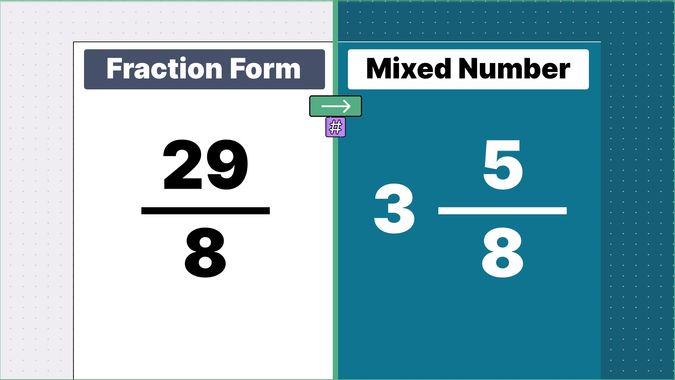
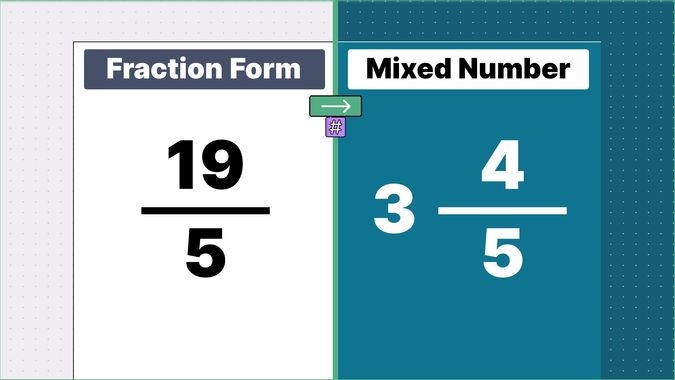
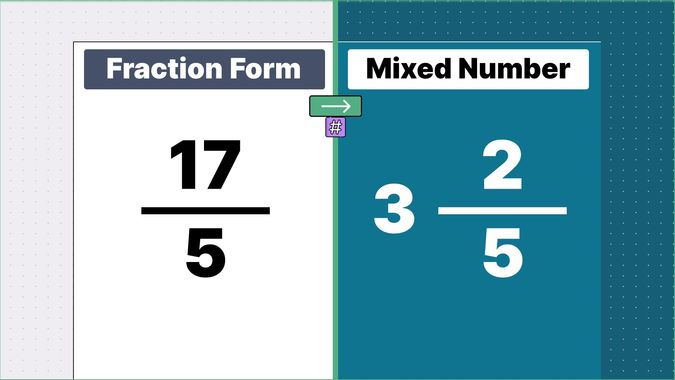
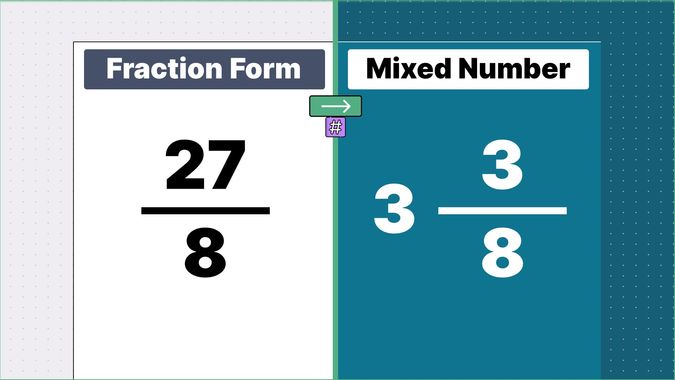
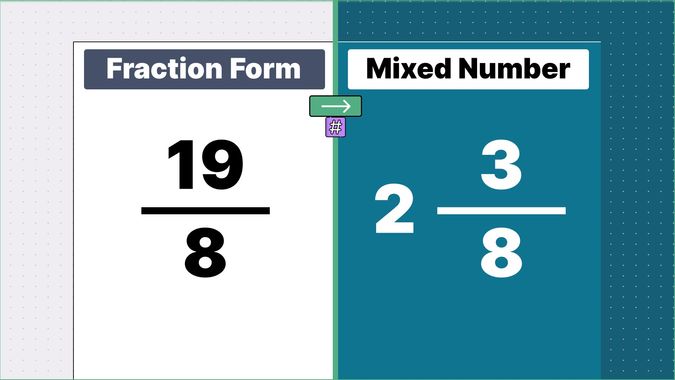
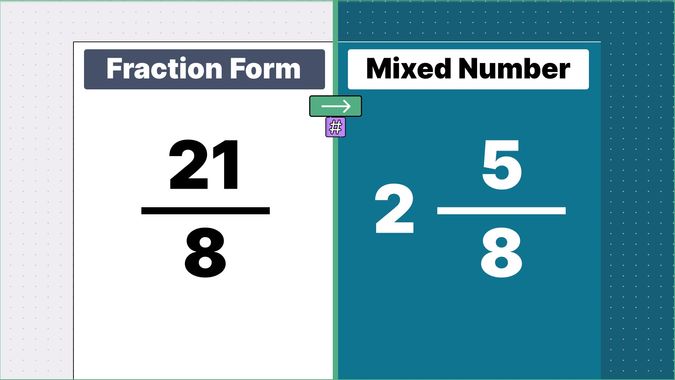
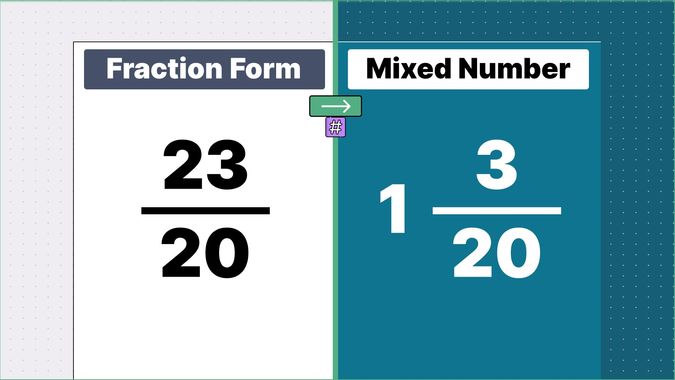
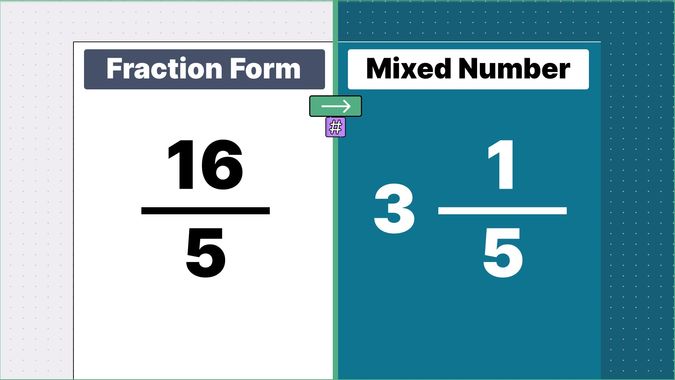
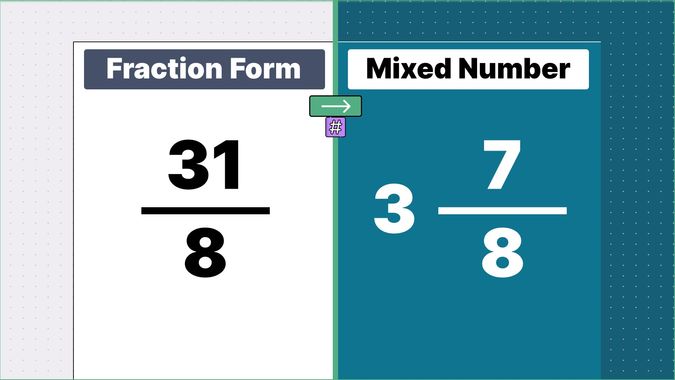
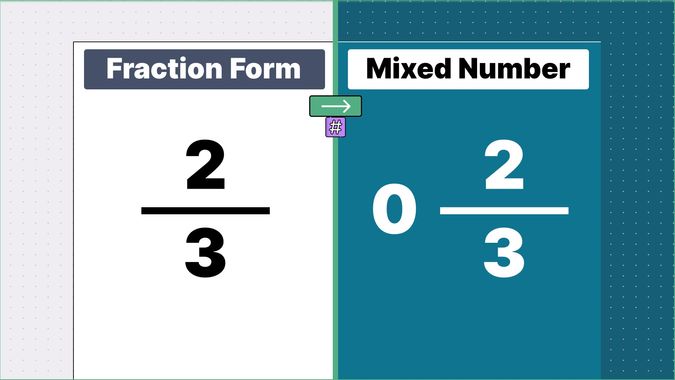
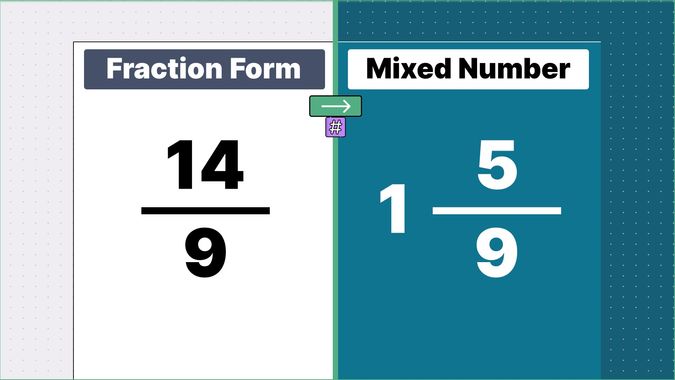
Other examples of fraction to mixed numbers